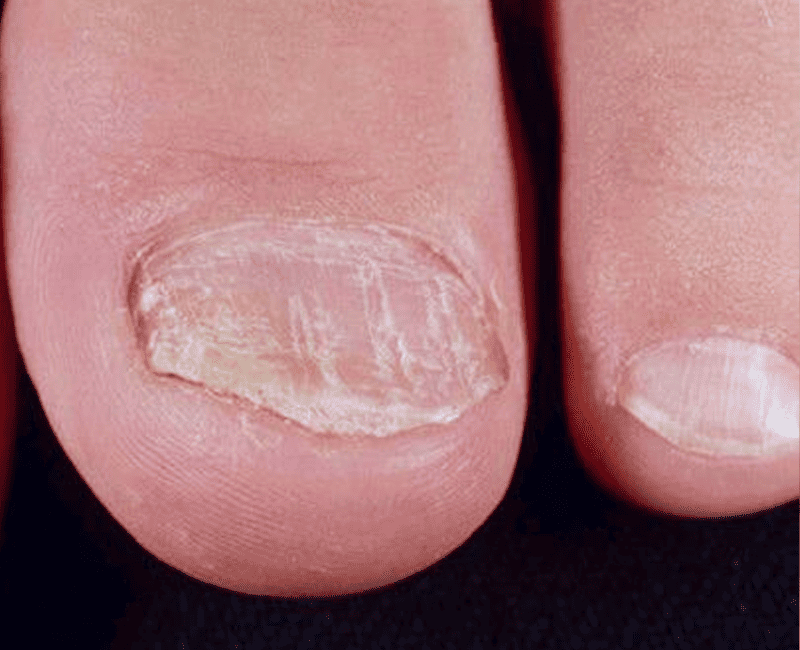
Nail psoriasis is a chronic condition affecting the fingernails and toenails, often linked to the autoimmune disorder psoriasis. This condition can cause a range of changes to the nails, including discoloration, pitting, thickening, and separation from the nail bed. Nail psoriasis can be both a cosmetic and functional concern, leading to discomfort and, in severe cases, impairing daily activities. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatments is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Nail psoriasis occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to an accelerated production of these cells. This abnormal growth affects the nails, resulting in the various symptoms associated with the condition. Several factors contribute to the development and exacerbation of nail psoriasis:
Nail psoriasis can manifest in various ways, depending on the severity and the specific areas of the nail affected. Common symptoms include:
Diagnosing nail psoriasis can be challenging because its symptoms often resemble other nail conditions, such as fungal infections or onychodystrophy. A dermatologist will typically conduct a physical examination of the nails and may take a detailed medical history to identify any family history of psoriasis or known triggers. In some cases, a biopsy of the nail or skin around the nail may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Nail psoriasis can be difficult to treat, especially because the nails grow slowly and treatments take time to show results. However, a variety of treatments are available that can help manage the symptoms and improve the appearance of the nails:
Living with Nail Psoriasis : Nail psoriasis can have a significant impact on daily life, particularly when it affects the ability to perform tasks that require fine motor skills, such as writing, typing, or buttoning clothes. The visible nature of nail psoriasis can also lead to self-consciousness and social anxiety. It is essential for individuals with nail psoriasis to seek support and work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition.
Nail psoriasis is a challenging condition that requires careful management and a personalized treatment approach. While it can be difficult to treat, especially in severe cases, there are a variety of options available that can help improve symptoms and enhance the appearance of the nails. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for preventing the condition from worsening and maintaining the health and function of the nails. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for nail psoriasis, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and lead a more comfortable, confident life.
Address:
Door No. 8-2-293/82/A/725/A, Beside FMS INTERNATIONAL DENTAL CENTER Road No. 37, Hitech City Rd, near Daspalla Hotel, CBI Colony, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad, Telangana 500033
Email: [email protected]
Email: [email protected]