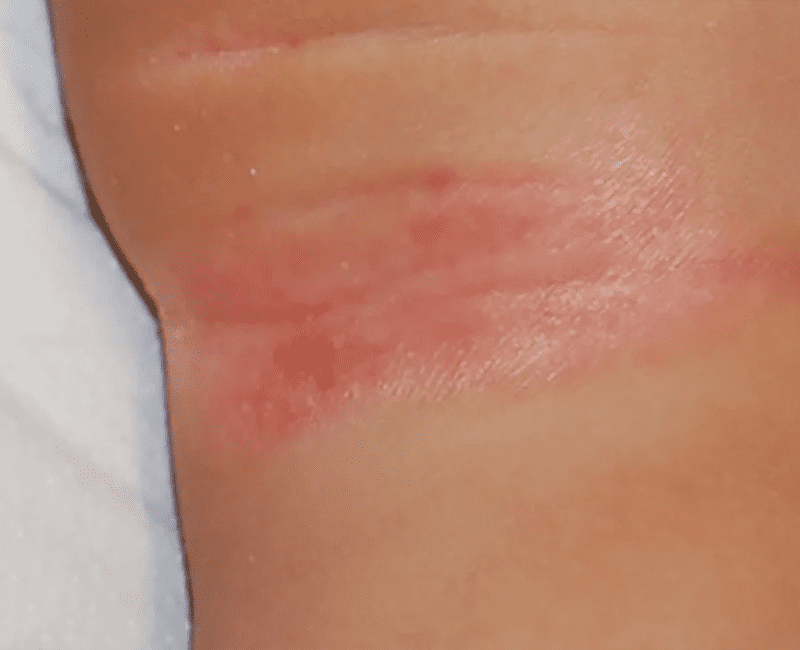
Flexural psoriasis, also known as inverse psoriasis, is a distinct type of psoriasis that primarily affects the skin folds or flexures, such as under the breasts, armpits, groin, and buttocks. Unlike the more common plaque psoriasis, which is characterized by thick, scaly plaques, flexural psoriasis presents as smooth, red, and shiny patches. The condition can be particularly uncomfortable due to the sensitive areas it affects, and it often poses unique challenges in diagnosis and treatment. This article provides an in-depth look at flexural psoriasis, exploring its causes, symptoms, management strategies, and the impact it can have on a person’s life.
Flexural psoriasis is a type of psoriasis that manifests in the body’s skin folds. The condition is marked by inflammation and redness in these areas, where the skin is thinner and more prone to irritation. Unlike other forms of psoriasis, flexural psoriasis does not usually produce the thick, silvery scales typical of plaque psoriasis. Instead, the affected areas appear smooth, shiny, and red.
The constant friction and moisture in the skin folds can exacerbate the symptoms, leading to discomfort and a higher risk of secondary infections, such as fungal or bacterial infections. Flexural psoriasis can occur in isolation or alongside other types of psoriasis, such as plaque or Guttate psoriasis.
The exact cause of flexural psoriasis, like other forms of psoriasis, is not fully understood. It is believed to be an immune-mediated condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, accelerating their turnover. Several factors contribute to the development and exacerbation of Flexural Psoriasis.
Flexural psoriasis presents with specific symptoms that distinguish it from other forms of psoriasis. Common symptoms include:
Diagnosing flexural psoriasis can be challenging because its appearance can be similar to other skin conditions that affect the skin folds, such as intertrigo, fungal infections, or eczema. A thorough examination by a dermatologist is essential for accurate diagnosis.
The dermatologist may perform the following steps:
Flexural psoriasis can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. The discomfort, itching, and potential pain associated with the condition can interfere with daily activities, sleep, and overall well-being. The visibility of the affected areas, particularly in intimate settings, can also lead to embarrassment and a negative self-image.
Psychologically, the chronic nature of flexural psoriasis can contribute to stress, anxiety, and depression. The need for ongoing management and the possibility of flare-ups can be mentally exhausting. Support from healthcare providers, as well as counselling or support groups, can be beneficial in managing the emotional impact of the condition.
Flexural psoriasis is a challenging and often uncomfortable condition that requires careful management. Understanding the unique aspects of this type of psoriasis, including its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, can empower individuals to take control of their condition. With the right combination of medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and emotional support, those with flexural psoriasis can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. On going research continues to offer hope for more effective treatments, paving the way for better outcomes in the future.
Address:
Door No. 8-2-293/82/A/725/A, Beside FMS INTERNATIONAL DENTAL CENTER Road No. 37, Hitech City Rd, near Daspalla Hotel, CBI Colony, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad, Telangana 500033
Email: [email protected]
Email: [email protected]