Maturity Melanosis, also known as senile lentigines or age spots, is a common skin condition characterized by the appearance of flat, dark patches on the skin, primarily in sun-exposed areas such as the face, hands, shoulders, and arms. These spots are a natural part of the aging process and are more prevalent in individuals over the age of 40. Maturity melanosis is considered a benign condition, meaning it is not harmful or cancerous, but it can be a cosmetic concern for those who develop these spots.
The primary cause of maturity melanosis is prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, which accelerates the production of melanin in the skin. Melanin is the pigment responsible for skin color, and when produced in excess, it can lead to the formation of dark spots. While this condition is not dangerous, it can be mistaken for other, more serious skin conditions, such as melanoma. Therefore, it is essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available for managing this condition.
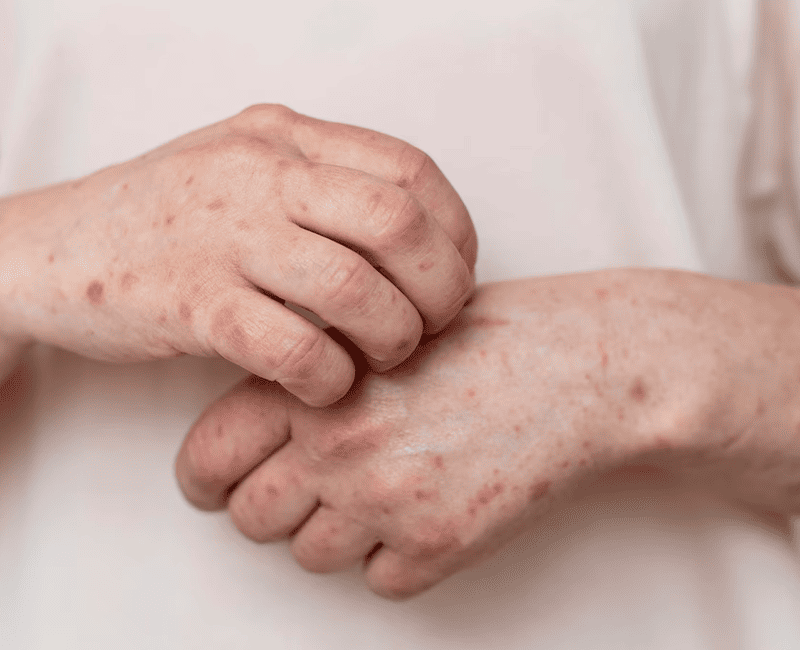
The exact cause of guttate psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This immune response triggers the rapid production of skin cells, leading to the formation of the characteristic lesions.
Several factors can contribute to the development of guttate psoriasis, including:
Diagnosing guttate psoriasis typically involves a physical examination of the skin by a dermatologist. The appearance of the lesions is often enough to make a diagnosis, especially if the patient has a history of a recent strep throat infection or other trigger factors.
In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. During a biopsy, a small sample of skin is taken and examined under a microscope to rule out other skin conditions that may resemble guttate psoriasis, such as pityriasis rosea or lichen planus.
Additionally, a throat swab or blood test may be done to check for a recent streptococcal infection, as treating the infection may help resolve the psoriasis flare-up.
Treatment for guttate psoriasis aims to reduce symptoms, clear the lesions, and prevent future flare-ups. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Common treatment options include:
Guttate psoriasis is a distinct form of psoriasis that can be triggered by infections, stress, and other factors. While it can be challenging to manage, various treatment options are available, ranging from topical treatments and phototherapy to systemic medications. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to controlling the condition and preventing complications. By working closely with a dermatologist and following a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals with guttate psoriasis can achieve significant improvement in their symptoms and enjoy a better quality of life.
Address:
Door No. 8-2-293/82/A/725/A, Beside FMS INTERNATIONAL DENTAL CENTER Road No. 37, Hitech City Rd, near Daspalla Hotel, CBI Colony, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad, Telangana 500033
Email: [email protected]
Email: [email protected]