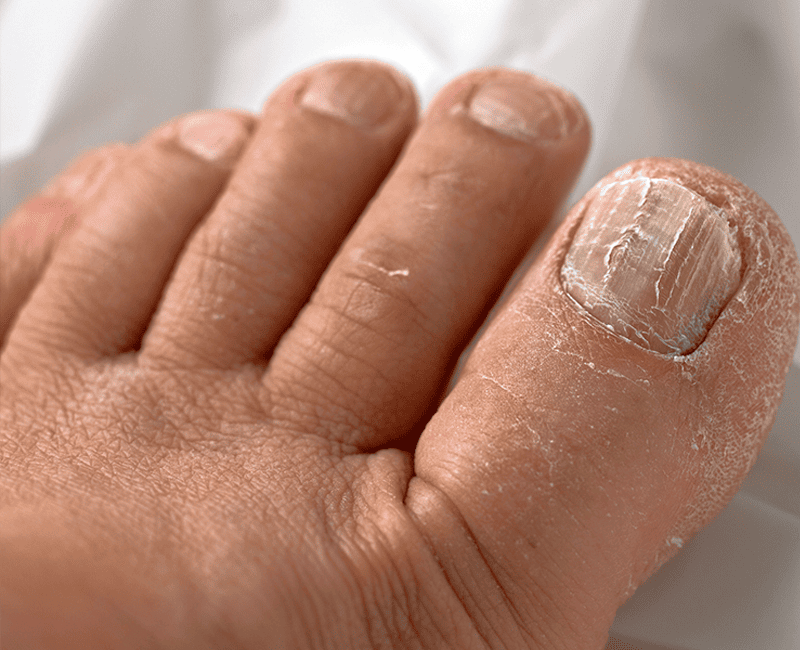
Nail fungal infection, also known as onychomycosis, is a common condition affecting the toenails and fingernails. It occurs when fungi, such as dermatophytes, yeast, or mold, infect the nail plate, nail bed, or surrounding skin. This condition often leads to thickened, discolored, brittle, or distorted nails, and while it may seem purely cosmetic, it can cause discomfort and may even spread to other nails or skin. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for nail fungal infections is crucial for effective management.
Nail fungal infections can be classified into several types based on the area affected and the characteristics of the infection:
Treating nail fungal infections can be challenging, as the infection is often deep-seated in the nail bed. The treatment approach may vary based on the severity of the infection, the type of fungus, and the patient’s health status. Here are the main treatment options available:
Prevention plays a crucial role in managing nail fungal infections, particularly for individuals who are prone to recurrent infections. Preventive measures include:
Address:
Door No. 8-2-293/82/A/725/A, Beside FMS INTERNATIONAL DENTAL CENTER Road No. 37, Hitech City Rd, near Daspalla Hotel, CBI Colony, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad, Telangana 500033
Email: [email protected]
Email: [email protected]